The “American tax UAE” situation for Americans has more to do with the IRS than the UAE. For Americans in the UAE, being in the country impacts their taxes primarily through US tax obligations. Dubai, the most populous city in the UAE, offers unparalleled experiences with its iconic skyscrapers, massive shopping malls, and bustling airports. However, if you’re an American considering relocating to Dubai, it’s essential to understand your US tax, Dubai. To understand the US taxation obligations in Dubai and UAE, begin with the IRS forms for Americans globally.
Is there even a tax on Dubai Salary for anybody? – clarify it here
American Tax UAE – The role of USA taxation in UAE
- As a US citizen or resident alien, your tax obligations follow you regardless of where you live.
- The United States taxes its citizens on worldwide income, which means that Americans living in Dubai must report their global income to the IRS.
- This obligation includes income earned in the UAE, interest, dividends, and capital gains.
The US tax for American expats in UAE: Obligations and Relief
1. The Annual Tax Return (Form 1040) is a form that US citizens and resident aliens use to report their income to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) annually. It includes details about your income, deductions, and credits to determine how much Tax you owe or how much of a refund you will receive. It helps the IRS calculate your tax liability for the year. All US citizens and resident aliens must file an annual tax return using Form 1040, regardless of residency.
2. Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows US citizens and resident aliens abroad to exclude a certain amount of their foreign-earned income from US taxation.
For example, in 2023, you could exclude up to $112,000 of your foreign-earned income, reducing the amount of income you must pay US taxes on. The form helps prevent double taxation on income earned outside the US.
Form 2555 ( a form to claim the FEIE) allows eligible expats to exclude up to $112,000 of foreign-earned income in 2023.
To qualify, you must meet one of two criteria:
- Physical Presence Test: You were physically present in a foreign country for at least 330 full days during 12 months.
- Bona Fide Residence Test: You were a bona fide resident of a foreign country for an entire tax year
The Foreign Housing Exclusion is a tax benefit available to FEIE-eligible Americans living abroad. It allows them to exclude certain housing expenses from their US taxable income.
3. Foreign Tax Credit (FTC): The Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) lets US citizens and residents lower their US taxes by the taxes they pay to foreign countries. If you pay taxes on your income in another country, the FTC can help you avoid paying taxes on that same income again in the US. It’s a way to prevent double taxation on income earned abroad. If you pay taxes in the UAE, you can claim a dollar-for-dollar credit against your US tax liability using Form 1116. However, it may not be beneficial in the UAE due to the absence of local income tax.
4. Foreign Bank Account Reporting (FBAR): FBAR requires US citizens and resident aliens to report foreign bank accounts and financial accounts if the total value of these accounts exceeds $10,000 at any time during the year. You can apply by filing FinCEN Form 114 online. The purpose is to help the US government detect and prevent tax evasion involving overseas accounts. If the aggregate value of your foreign financial accounts exceeds $10,000 at any time during the year, you must file FinCEN Form 114.
5. Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA): FATCA is a law that requires US citizens and resident aliens to report certain foreign financial assets if their value exceeds specific thresholds. You can apply by using Form 8938. FATCA also requires foreign financial institutions to report information about accounts held by US taxpayers to the IRS. The goal is to prevent tax evasion by US citizens using foreign accounts.
6. Self-Employment Tax: Self-Employment Tax is a tax levied by the US that self-employed Americans must pay to cover Social Security and Medicare taxes. If you are self-employed and your net earnings are $400 or more, you must pay this Tax. It applies to your earnings from self-employment, regardless of where you live, including as an American in Dubai.
7. State Taxes: State taxes are taxes imposed by individual US states. US state taxes can affect American Tax UAE if they are still considered residents of a state that imposes income tax. These taxes can include Income Tax, Sales Tax, Property Tax, Excise Tax, Corporate Tax
Each state has its tax laws, and some do not impose certain taxes. You might be subject to state taxes if you maintain a domicile in a US state with an income tax. It’s essential to clarify your residency status to avoid unexpected liabilities.
Finding our VAT Registration & Consultancy Services content interesting?
world-class services.
THE FIRST CONSULTATION IS FREE!
Critical Deadlines for US Tax Dubai, UAE and worldwide
1. April 15: Taxes are due, but expatriates get an automatic extension to June 15. However, interest on any owed taxes starts accruing on April 15.
2. June 15: This is the automatic extension for US expatriate taxes unless you file further extensions.
3. June 30: Deadline for submitting the FBAR form.
4. October 15: Final deadline for all expatriate taxes.
Dubai Tax Environment
Dubai offers a tax-free personal income environment. It has no capital gains tax and no inheritance tax, making it an attractive destination for expatriates and investors. Dubai also offers a highly favourable tax environment for residents and businesses, contributing to its attractiveness as a global business hub.

American tax UAE resident
Even as a UAE tax resident, you must file US tax returns and report any income earned across the globe. However, you can benefit from the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) and Foreign Housing Exclusion, which reduce US taxable income if you meet the eligibility requirements. The Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) can also help if you pay taxes to other countries. Additionally, depending on your home state’s laws, you are free of state tax obligations if you have severed residency ties with the particular state.
UAE Tax Residency Criteria
Individuals in the UAE are tax residents if they meet any of the following:
- You have lived in the UAE for at least 183 days in a calendar year.
- Your stay is continuous and meets the 183-day requirement over 12 months.
- You hold a valid residence visa.
Types of Taxes in the UAE
Understanding the local tax environment is crucial for Americans residing in the UAE, even though the country is known for its minimal personal income tax. While the UAE does not impose direct income tax on individuals, it does have other taxes that can impact residents and businesses. These include Value Added Tax (VAT), Corporate Tax (CT), and export taxes. VAT applies to most goods and services, Corporate Tax affects certain businesses, and export taxes may apply to goods leaving the country. Familiarity with these taxes is essential for effective financial planning and compliance.
Value-Added Tax (VAT)
VAT is a general tax on the UAE’s consumption of goods and services. It applies to all businesses and consumers, including American expats and tax residents.
Introduced on January 1, 2018, the UAE’s VAT rate is 5%. Businesses must register for VAT if their taxable supplies and imports exceed AED 375,000 annually. VAT registration is optional for those with taxable supplies and imports between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000. Businesses can deregister if their taxable supplies fall below AED 187,500 for a year. Certain items, such as exports outside the Gulf Cooperation Council, international transportation, and specific education and healthcare services, may be taxed at 0%.
Corporate Tax
This Tax applies to specific sectors, such as upstream oil and gas companies and foreign bank branches, and a general corporate tax rate for companies operating in the UAE. Regardless of the owner’s nationality, it affects any registered business or occupation. While most companies in the UAE are not subject to corporate Tax, exceptions include:
– Upstream oil and gas companies are taxed at rates up to 55%.
– Foreign bank branches are taxed at a flat rate of 20%.
A corporate tax rate of 9% applies to all companies operating in the UAE.
Know more about the Corporate Tax and how it may impact you, here.
Excise Tax
The UAE imposes an excise tax on goods harmful to health, including tobacco products, electronic smoking devices, energy drinks, carbonated drinks, and sweetened drinks. The excise tax applies to all consumers and businesses within the UAE, including American expats and other residents.
Double Taxation Agreements
The US tax Dubai or the USA taxation of Dubai or the rest of UAE is complex because of the absence of a double taxation agreement. The US and UAE do not have a tax treaty, meaning you would pay double taxes if careful. However, the FTC and FEIE can help mitigate the risk of double taxation. The UAE has tax treaties with many countries but not with the US.
To avoid paying double taxes in both the US and the UAE, one could:
– Spend less than 183 days in the UAE annually.
– Stay outside the US for at least 330 days in 12 months.
– Ensure income does not exceed the FEIE limit.
FAQs
1. Do Americans pay US tax Dubai?
2. What is the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE)?
3. Is there a tax treaty between the US and UAE?
4. What are the implications for self-employed American Tax Dubai?
5. Who Needs to Pay American Tax UAE?
7. Do foreigners pay tax in UAE?
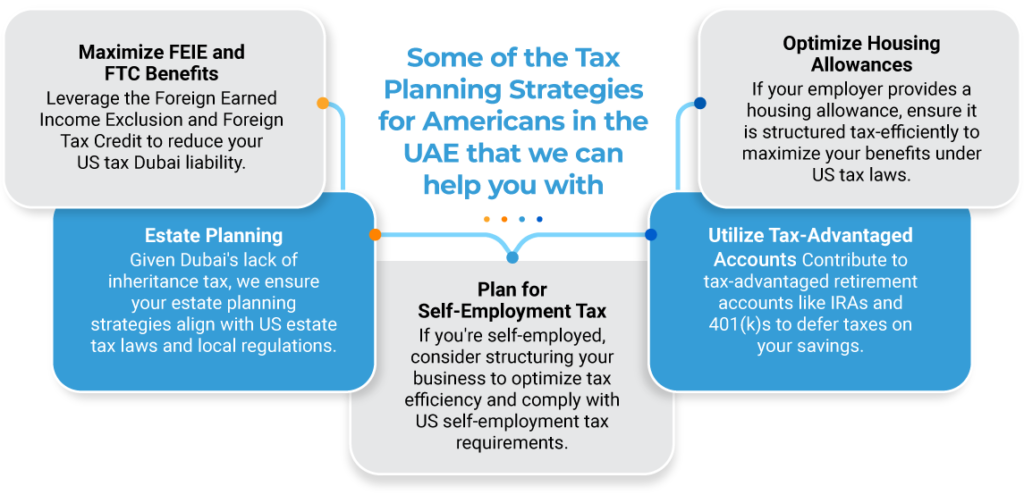
Some of the Tax Planning Strategies for Americans in the UAE that we can help you with
1. Maximize FEIE and FTC Benefits: Leverage the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion and Foreign Tax Credit to reduce your US tax Dubai liability.
2. Optimize Housing Allowances: If your employer provides a housing allowance, ensure it is structured tax-efficiently to maximize your benefits under US tax laws.
3. Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Contribute to tax-advantaged retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s to defer taxes on your savings.
4. Plan for Self-Employment Tax: If you’re self-employed, consider structuring your business to optimize tax efficiency and comply with US self-employment tax requirements.
5. Estate Planning: Given Dubai’s lack of inheritance tax, we ensure your estate planning strategies align with US estate tax laws and local regulations.
Consider consulting with an expat tax expert for personalized advice on your tax situation. We are ready to assist you with any concerns. Contact us today to learn more.




